【CoppeliaSim|V |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › catia运动仿真教程机械臂 › 【CoppeliaSim|V |
【CoppeliaSim|V
【CoppeliaSim|V-REP|教程(一)】零基础如何快速入门 Coppeliasim(原V-REP)并实现机械臂的正逆解和轨迹规划仿真(附源码注释解析)
 宇宙爆肝锦标赛冠军
分类:建模仿真
个人专栏:coppeliaSim 发布时间 2021.08.16阅读数 16682 评论数 5
0. 前言
之前使用ROS主要是做移动机器人,认为自己的ROS已经用的很熟练了,但是接触机械臂后,发现 Moveit 使用起来没有那么方便,在学长的建议下,开始使用 Coppeliasim。
Coppeliasim 就是曾经大名鼎鼎的 V-rep,提供了 Lua、C++、Python、ROS1、ROS2 等 API接口,十分方便,而且仿真速度很快,模型渲染的也不错,相比于 Gazebo 中的 URDF 模型,其更容易上手。
1. 软件版本区别
宇宙爆肝锦标赛冠军
分类:建模仿真
个人专栏:coppeliaSim 发布时间 2021.08.16阅读数 16682 评论数 5
0. 前言
之前使用ROS主要是做移动机器人,认为自己的ROS已经用的很熟练了,但是接触机械臂后,发现 Moveit 使用起来没有那么方便,在学长的建议下,开始使用 Coppeliasim。
Coppeliasim 就是曾经大名鼎鼎的 V-rep,提供了 Lua、C++、Python、ROS1、ROS2 等 API接口,十分方便,而且仿真速度很快,模型渲染的也不错,相比于 Gazebo 中的 URDF 模型,其更容易上手。
1. 软件版本区别
CoppeliaSim 各个版本官方下载:https://www.coppeliarobotics.com/previousVersions
英文:https://www.coppeliarobotics.com/helpFiles/ API 函数手册:在官方手册的该目录下(Writing code in and around CoppeliaSim-->CoppeliaSim API framework-->Regular API reference) API 常量手册:在官方手册的该目录下(Writing code in and around CoppeliaSim-->CoppeliaSim API framework-->Regular API constants) IK plugin API 手册:https://www.coppeliarobotics.com/helpFiles/en/simIK.htm Remote API functions (Lua)手册:https://www.coppeliarobotics.com/helpFiles/en/remoteApiFunctionsLua.htm OMPL Plugin API reference 手册:在官方教程的该目录下(Functionality/Path planning/simOMPL API reference) 常用 API 汇总:https://mde.tw/copsim_manual/content/apiOverview.htm中文 上半部分:https://blog.csdn.net/Csdn_Darry/article/details/107142216 下半部分:https://blog.csdn.net/Csdn_Darry/article/details/109023538 2.2 官方论坛 Forum——Questions/Answers around CoppeliaSim/V-REP 很多示例代码的参数不理解,都可以在官方论坛上找到,而百度几乎检索不到你想要解决的问题。 2.3 网友的应用教程:作为一款仿真工具,大家的研究重点并不是该软件的众多功能,而是快速搭建仿真场景,验证自己的机器视觉、轨迹规划、运动控制等算法,下面贴出了一些网友给出的教程,供大家参考。 以UR5为例浅析V-REP中的逆向运动学 用UR5进行识别、抓取和码垛 V-rep机器人仿真(Win10):UR5+RG2+Kinect+YOLOV3+DDPG+Pytorch 第一部分:Vrep基本操作 第二部分:Vrep与python的联调 第三部分:在V-rep中用python控制机械臂 第四部分:YOLOV3图像识别 第五部分:YOLOV3与V-rep V-REP(CoppeliaSim)自学笔记 机械臂末端沿既定的轨迹运动 Vrep/CoppeliaSim_沿path运动(上):逆运动学 Vrep/CoppeliaSim_沿path运动(下):设置path 2.4 Lua 教程 Lua 菜鸟教程:https://www.runoob.com/lua/lua-tutorial.html Coppeliasim Lua 脚本常用的语法: “#”的含义 3. 关于机械臂的入门 3.1 几个重要的 API 正逆解 API——simIK:仅仅得到正逆解是无法得到机械臂的整个运动轨迹的。 轨迹规划 API——simOMPL:用于实现机械臂的分段插值,实现轨迹的近似连续,百度几乎搜不到相关的使用教程。 3.2 几个重要的官方范例 ik_fk_simple_examples.ttt
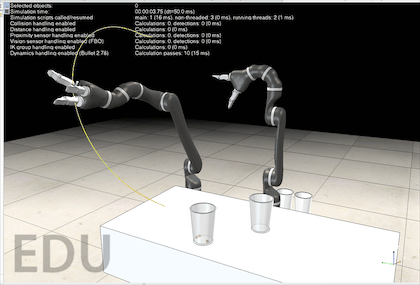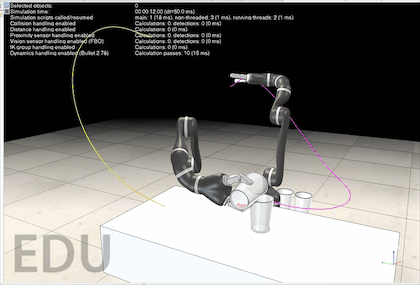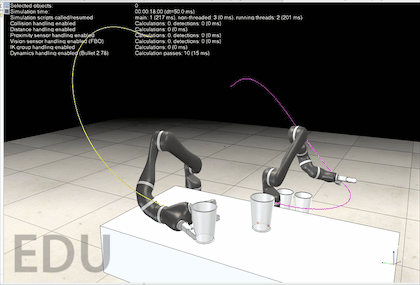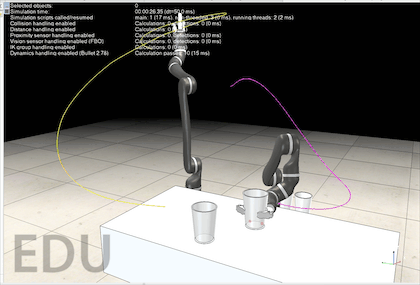
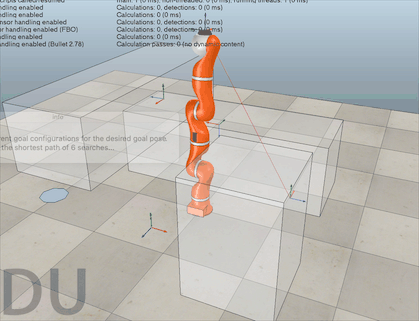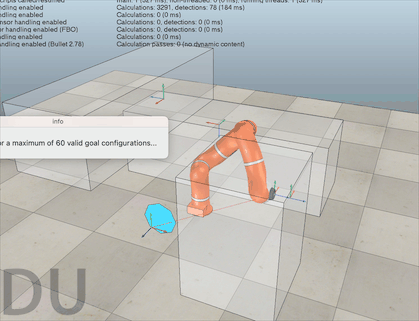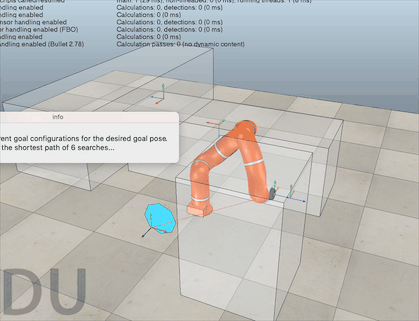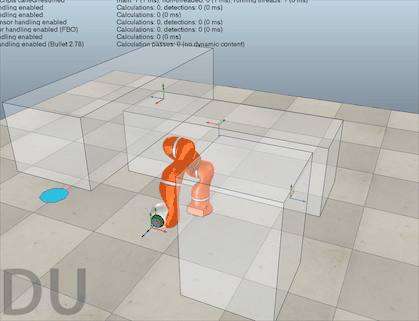
对于机械臂的轨迹规划,课本中学的是七次轨迹规划或者是分段轨迹规划,但这样仍然可能会有找不到逆解的时候。Coppeliasim 官方提供了的 motionplanningserverdemo.ttt 这个场景文件中,有一个轨迹规划的服务可供调用。打开这个场景运行后,大家可能看不到机械臂的任何运动,因为代码中并没有调用那些服务,需要自己在机械臂的脚本中调用。
源码都是好几百行,可能大家很想知其所然,这里贴出我在阅读 motionPlanningDemo1.ttt 的源码时添加的注释,帮助大家理解。阅读过程中的API函数均可以在官方教程中找到。 该源码的每一行我都有阅读,可以尝试在 sysCall_threadmain() 中注释掉一些代码,然后运行程序,这样可以帮助大家理解每个函数的功能。 如果对该代码实现的功能存在疑问,欢迎在评论区留言,我会尽可能回复大家! -- 显示信息 displayInfo=function(txt) if dlgHandle then sim.endDialog(dlgHandle) end dlgHandle=nil if txt and #txt>0 then dlgHandle=sim.displayDialog('info',txt,sim.dlgstyle_message,false) sim.switchThread() end end -- 返回沿矩阵z轴通过localZShift移动的姿势或矩阵 getMatrixShiftedAlongZ=function(matrix,localZShift) -- Returns a pose or matrix shifted by localZShift along the matrix's z-axis local m={} for i=1,12,1 do m[i]=matrix[i] end m[4]=m[4]+m[3]*localZShift m[8]=m[8]+m[7]*localZShift m[12]=m[12]+m[11]*localZShift return m end -- 允许或禁止自动线程切换。这对于线程脚本可能很重要。例如,您不希望在临时修改机器人配置时发生切换,因为这样您将在场景显示中看到该更改。 forbidThreadSwitches=function(forbid) -- Allows or forbids automatic thread switches. -- This can be important for threaded scripts. For instance, -- you do not want a switch to happen while you have temporarily -- modified the robot configuration, since you would then see -- that change in the scene display. if forbid then forbidLevel=forbidLevel+1 if forbidLevel==1 then sim.setThreadAutomaticSwitch(false) end else forbidLevel=forbidLevel-1 if forbidLevel==0 then sim.setThreadAutomaticSwitch(true) end end end -- 这里我们搜索机器人配置 -- 1…匹配所需姿势(矩阵) -- 2…在该配置中不会发生冲突 -- 3…不会发生碰撞,并且可以执行IK线性逼近 findCollisionFreeConfigAndCheckApproach=function(matrix) -- Here we search for a robot configuration.. -- 1. ..that matches the desired pose (matrix) -- 2. ..that does not collide in that configuration -- 3. ..that does not collide and that can perform the IK linear approach sim.setObjectMatrix(ikTarget,-1,matrix) -- ikTarget 移动到 matrix 的位姿 -- Here we check point 1 & 2: local c=sim.getConfigForTipPose(ikGroup,jh,0.65,10,nil,collisionPairs) -- 搜索与空间中目标虚拟对象位置/方向匹配的操纵器配置。 if c then -- Here we check point 3: local m=getMatrixShiftedAlongZ(matrix,ikShift) -- 齐次矩阵沿着z轴移动 ikShift 的距离 local path=generateIkPath(c,m,ikSteps) -- 生成目标配置和沿z轴移动一段距离后的点之间的直线路径 if path==nil then -- 如果不存在直线路径 c=nil -- 则不存在相应的关节配置 end end return c -- 返回关节配置 end --这里我们搜索几个机器人配置 --1…匹配所需姿势(矩阵) --2…在该配置中不会发生冲突 --3…不会发生碰撞,并且可以执行IK线性逼近 -- param 1: -- param 2: 尝试搜索次数 -- param 3: 搜索到的配置数量不超过该值 -- return: 搜索到的关节配置的集合 findSeveralCollisionFreeConfigsAndCheckApproach=function(matrix,trialCnt,maxConfigs) -- Here we search for several robot configurations... -- 1. ..that matches the desired pose (matrix) -- 2. ..that does not collide in that configuration -- 3. ..that does not collide and that can perform the IK linear approach forbidThreadSwitches(true) sim.setObjectMatrix(ikTarget,-1,matrix) -- 将 ikTarget 移动到 matrix local cc=getConfig() -- 各个关节当前配置 local cs={} local l={} for i=1,trialCnt,1 do local c=findCollisionFreeConfigAndCheckApproach(matrix) -- 搜索到matrix的关节配置c if c then -- 如果关节配置存在 local dist=getConfigConfigDistance(cc,c) -- 求cc和c之间的距离 local p=0 -- 好像没有用到这个变量? local same=false -- 初始化bool变量,用于记录新搜索到的配置是否与搜索历史不同 -- 检查新搜索到的关节配置c是否与曾经搜索的配置中的某个相同,若不同则作为新的配置加入集合 for j=1,#l,1 do if math.abs(l[j]-dist)0.01 then same=false break end end end if same then break end end if not same then -- 如果不相同 cs[#cs+1]=c -- 新搜索到的关节配置加入cs l[#l+1]=dist -- 当前关节配置和新搜索到的关节配置之间的距离加入l end end if #l>=maxConfigs then -- 如果已经搜索到足够多的新配置 break -- 则退出搜索 end end forbidThreadSwitches(false) if #cs==0 then -- 如果没有搜索到新的关节配置 cs=nil -- 则 cs 为空 end return cs -- 返回新的关节配置集合 end -- 返回当前机器人配置 getConfig=function() -- Returns the current robot configuration local config={} for i=1,#jh,1 do config[i]=sim.getJointPosition(jh[i]) end return config end -- 将指定的配置应用于机器人 setConfig=function(config) -- Applies the specified configuration to the robot if config then for i=1,#jh,1 do sim.setJointPosition(jh[i],config[i]) end end end -- 返回两个配置之间的距离(在配置空间中) -- 利用勾股定理求不同关节配置之间末端的欧氏距离 getConfigConfigDistance=function(config1,config2) -- Returns the distance (in configuration space) between two configurations local d=0 for i=1,#jh,1 do local dx=(config1[i]-config2[i])*metric[i] d=d+dx*dx end return math.sqrt(d) end -- 返回配置空间中路径的长度 getPathLength=function(path) -- Returns the length of the path in configuration space local d=0 local l=#jh local pc=#path/l for i=1,pc-1,1 do local config1={path[(i-1)*l+1],path[(i-1)*l+2],path[(i-1)*l+3],path[(i-1)*l+4],path[(i-1)*l+5],path[(i-1)*l+6],path[(i-1)*l+7]} local config2={path[i*l+1],path[i*l+2],path[i*l+3],path[i*l+4],path[i*l+5],path[i*l+6],path[i*l+7]} d=d+getConfigConfigDistance(config1,config2) end return d end -- 沿着指定的路径点运动。每个路径点都是机器人配置。这里我们不做任何插值 followPath=function(path) -- Follows the specified path points. Each path point is a robot configuration. Here we don't do any interpolation if path then local l=#jh local pc=#path/l -- 将关节角设置为路径上插值点的关节配置 for i=1,pc,1 do local config={path[(i-1)*l+1],path[(i-1)*l+2],path[(i-1)*l+3],path[(i-1)*l+4],path[(i-1)*l+5],path[(i-1)*l+6],path[(i-1)*l+7]} setConfig(config) sim.switchThread() -- 允许当前线程显式中断执行,并将控制权交还给CoppeliaSim,紧挨着抢占式线程 end end end -- 在这里,我们在指定的开始和目标配置之间进行路径规划。我们运行搜索cnt次,并返回最短路径及其长度 findPath=function(startConfig,goalConfigs,cnt) -- Here we do path planning between the specified start and goal configurations. We run the search cnt times, -- and return the shortest path, and its length local task=simOMPL.createTask('task') simOMPL.setAlgorithm(task,simOMPL.Algorithm.RRTConnect) local j1_space=simOMPL.createStateSpace('j1_space',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.joint_position,jh[1],{-170*math.pi/180},{170*math.pi/180},1) local j2_space=simOMPL.createStateSpace('j2_space',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.joint_position,jh[2],{-120*math.pi/180},{120*math.pi/180},2) local j3_space=simOMPL.createStateSpace('j3_space',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.joint_position,jh[3],{-170*math.pi/180},{170*math.pi/180},3) local j4_space=simOMPL.createStateSpace('j4_space',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.joint_position,jh[4],{-120*math.pi/180},{120*math.pi/180},0) local j5_space=simOMPL.createStateSpace('j5_space',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.joint_position,jh[5],{-170*math.pi/180},{170*math.pi/180},0) local j6_space=simOMPL.createStateSpace('j6_space',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.joint_position,jh[6],{-120*math.pi/180},{120*math.pi/180},0) local j7_space=simOMPL.createStateSpace('j7_space',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.joint_position,jh[7],{-170*math.pi/180},{170*math.pi/180},0) simOMPL.setStateSpace(task,{j1_space,j2_space,j3_space,j4_space,j5_space,j6_space,j7_space}) simOMPL.setCollisionPairs(task,collisionPairs) simOMPL.setStartState(task,startConfig) simOMPL.setGoalState(task,goalConfigs[1]) for i=2,#goalConfigs,1 do simOMPL.addGoalState(task,goalConfigs[i]) end local path=nil -- 最短的路径 local l=999999999999 -- 路径的最短长度 forbidThreadSwitches(true) -- 禁止自动线程切换 -- 计算 cnt 次可行路径,并得到最短的一条 for i=1,cnt,1 do local res,_path=simOMPL.compute(task,4,-1,300) -- 计算得到路径 if res and _path then local _l=getPathLength(_path) if _l4 then -- 如果索引大于 4 targetIndex=1 -- 则复位到第 1 个目标索引 end -- m是当前目标的变换矩阵或姿势: -- m is the transformation matrix or pose of the current target: local m=sim.getObjectMatrix(theTarget,-1) -- 计算ikDist沿姿势m的Z轴移动的姿势,以便我们有一个沿目标轴Z线性的最终方法: -- Compute a pose that is shifted by ikDist along the Z-axis of pose m, -- so that we have a final approach that is linear along target axis Z: m=getMatrixShiftedAlongZ(m,-ikShift) -- 找到姿势m的几个配置,并根据到当前配置的距离进行排序(距离越小越好)。在以下函数中,我们还检查碰撞以及最终IK方法是否可行: -- Find several configs for pose m, and order them according to the -- distance to current configuration (smaller distance is better). -- In following function we also check for collisions and whether the -- final IK approach is feasable: displayInfo('searching for a maximum of 60 valid goal configurations...') local c=findSeveralCollisionFreeConfigsAndCheckApproach(m,300,60) -- 当前目标对应的关节配置的集合 -- 搜索从当前配置到目标配置的路径。对于每个目标配置,搜索6次路径并保持最短路径。 -- 对findCollisionFreeConfigs返回的前3个配置执行此操作。 -- 由于我们不希望沿负Z轴接近,我们在场景中放置了一个人工障碍物(蓝色正交): -- Search a path from current config to a goal config. For each goal -- config, search 6 times a path and keep the shortest. -- Do this for the first 3 configs returned by findCollisionFreeConfigs. -- Since we do not want an approach along the negative Z axis, we place -- an artificial obstacle into the scene (the blue orthogon): local initialApproachDirectionObstaclePose=sim.getObjectMatrix(approachDirectionObstacle,-1) -- 暂存 approachDirectionObstacle 的齐次矩阵 sim.setObjectPosition(approachDirectionObstacle,theTarget,{0,0,-ikShift+0.01}) -- 设置 approachDirectionObstacle 相对当前目标的位置 sim.setObjectOrientation(approachDirectionObstacle,theTarget,{0,0,0}) -- 设置 approachDirectionObstacle 相对当前目标的四元数 sim.switchThread() -- in order see the change before next operation locks local txt='Found '..#c..' different goal configurations for the desired goal pose.' txt=txt..'&&nNow searching the shortest path of 6 searches...' displayInfo(txt) local path=findShortestPath(getConfig(),c,6) -- 搜索当前关节配置和当前目标的关节配置之间的最短路径,共搜索 6 次 displayInfo(nil) sim.setObjectMatrix(approachDirectionObstacle,-1,initialApproachDirectionObstaclePose) -- 恢复 approachDirectionObstacle 的齐次矩阵 -- 走这条路 -- Follow the path: followPath(path) -- 对于最终进近,目标是原始目标姿势: -- For the final approach, the target is the original target pose: m=sim.getObjectMatrix(theTarget,-1) -- 计算从当前配置到姿势m的直线路径: -- Compute a straight-line path from current config to pose m: path=generateIkPath(getConfig(),m,ikSteps) -- Follow the path: followPath(path) -- 生成反向路径以便向后移动: -- Generate a reversed path in order to move back: path=getReversedPath(path) -- Follow the path: followPath(path) end end V-REP机械臂应用实战轨迹规划机械臂仿真机器人建模仿真原创文章作者:宇宙爆肝锦标赛冠军。如若转载,请注明出处:古月居 https://www.guyuehome.com/34817 打赏 2 点赞 8 收藏 14 分享 微信 微博 QQ 图片 下一篇:【工业机器人|知识要点(一)】绪论 & 机电一体化结构 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |