sklearn:auc、roc |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › auc的功能 › sklearn:auc、roc |
sklearn:auc、roc
|
sklearn.metrics.auc
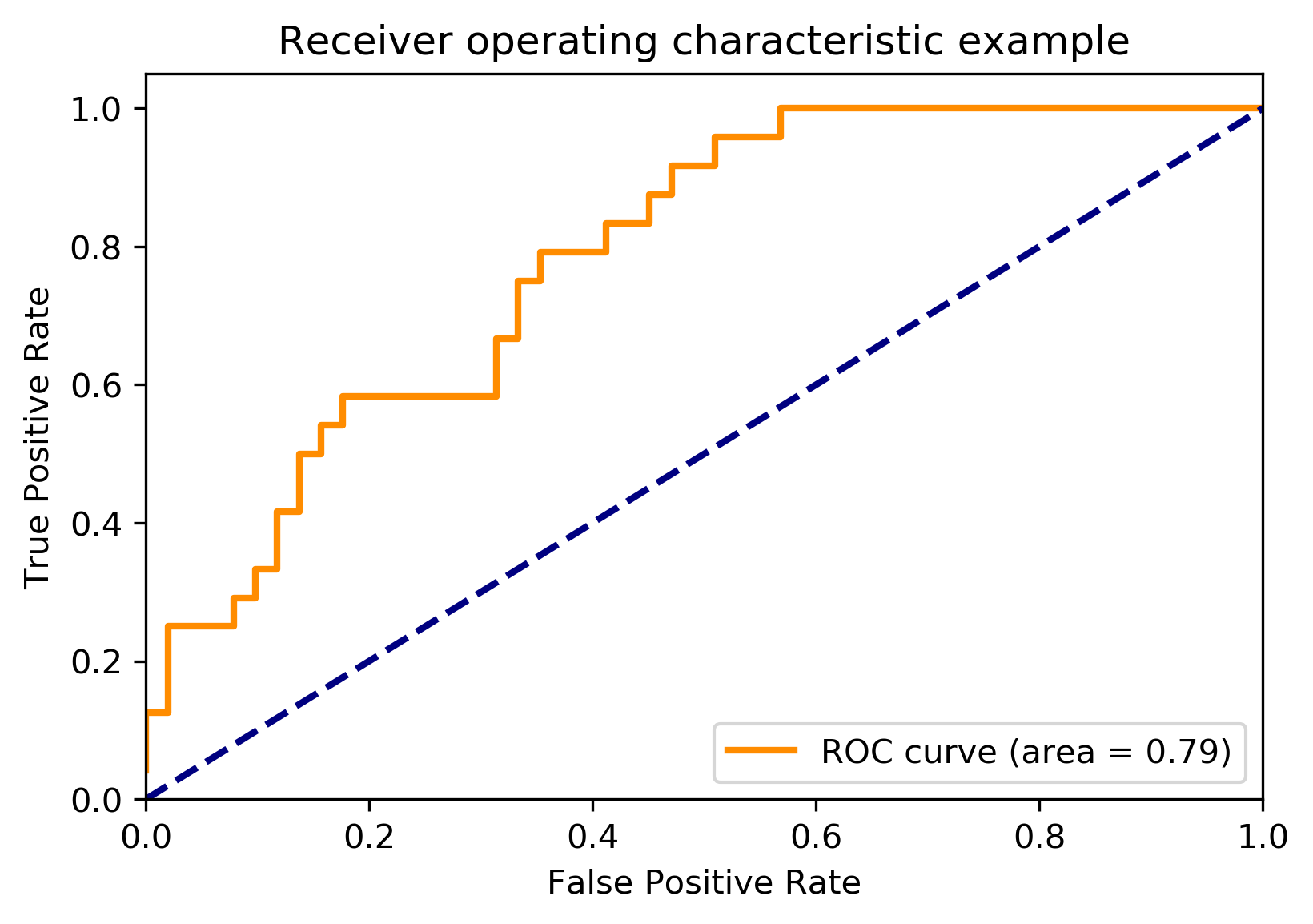
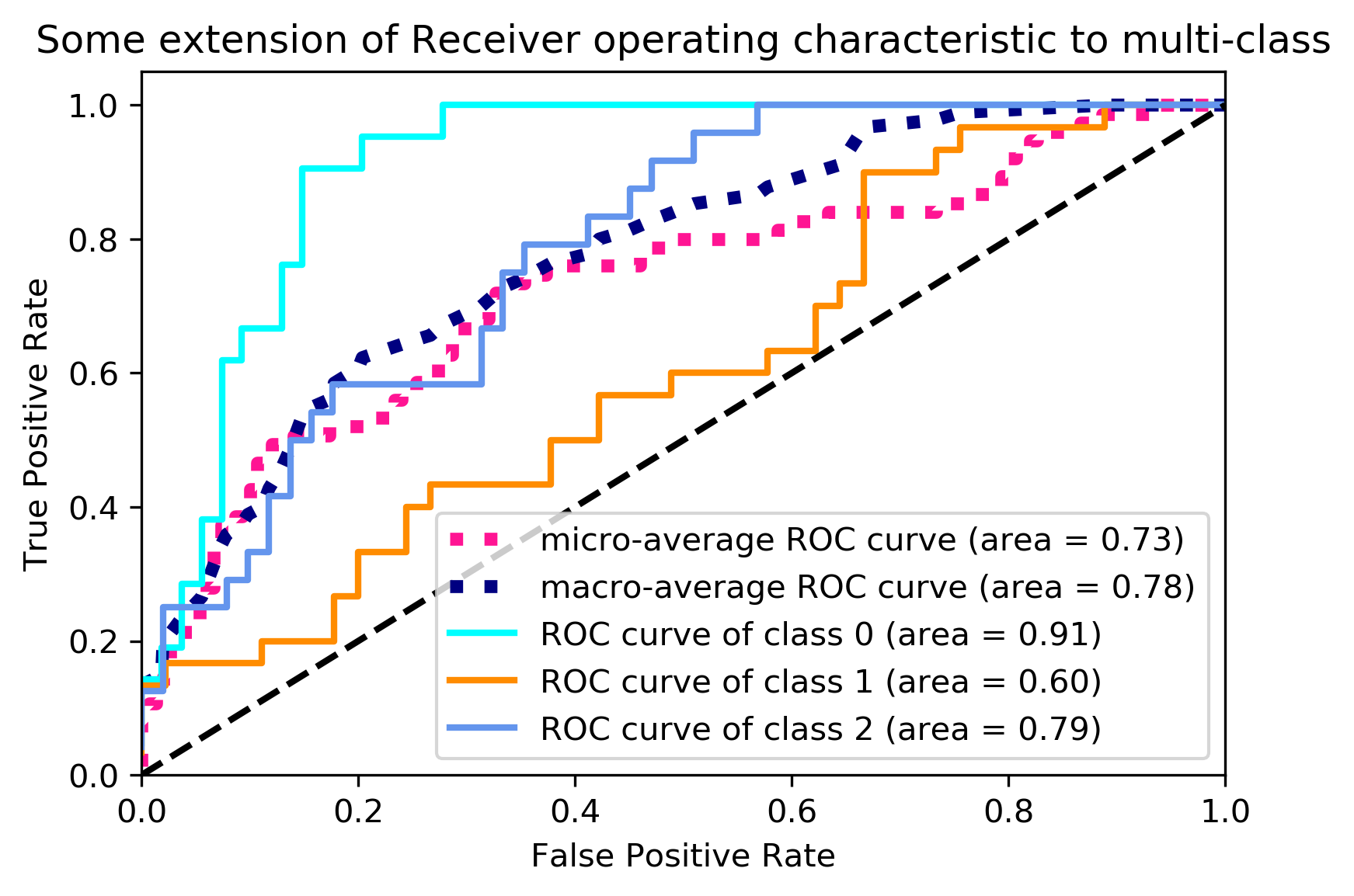
作用:计算AUC(Area Under the Curve) metrics.roc_curve作用:计算 ROC(Receiver operating characteristic) 注意: this implementation is restricted to the binary classification task sklearn.metrics.roc_curve(y_true, y_score, pos_label=None, sample_weight=None, drop_intermediate=True) parameter :y_true : array, shape = [n_samples] True binary labels. If labels are not either {-1, 1} or {0, 1}, then pos_label should be explicitly given y_score : array, shape = [n_samples] pos_label : int or str, default=None , Label considered as positive and others are considered negative. Returns fpr : false positive ratestpr : true positive ratesthresholds : array, shape = [n_thresholds]例子: pos_label = 1即表示标签为1的是正样本,其余的都是负样本,因为这个只能做二分类。 import numpy as np from sklearn import metrics y = np.array([1, 1, 2, 2,3,3]) pred = np.array([0.1, 0.4, 0.35, 0.8,0.1,0.8]) fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(y, pred, pos_label = 1) metrics.auc(fpr, tpr) 0.3125 sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score作用:Compute Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC AUC) from prediction scores 注意:this implementation is restricted to the binary classification task or multilabel classification task inlabel indicator format. sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, average=’macro’, sample_weight=None, max_fpr=None) Parameters:y_true : array, shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_classes] y_score : array, shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_classes] average : string, [None, ‘micro’, ‘macro’ (default), ‘samples’, ‘weighted’],If None, the scores for each class are returned. Otherwise, this determines the type of averaging performed on the data。 Returns:auc : float ### roc_auc_score import numpy as np from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1]) y_scores = np.array([0.1, 0.4, 0.35, 0.8]) roc_auc_score(y_true, y_scores) 0.75roc_auc_score 是 预测得分曲线下的 auc,在计算的时候调用了 auc; def _binary_roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, sample_weight=None): if len(np.unique(y_true)) != 2: raise ValueError("Only one class present in y_true. ROC AUC score " "is not defined in that case.") fpr, tpr, tresholds = roc_curve(y_true, y_score, sample_weight=sample_weight) return auc(fpr, tpr, reorder=True)所以不能用在多分类问题上。 多分类问题的auc计算例子: import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from itertools import cycle from sklearn import svm,datasets from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import label_binarize from sklearn.multiclass import OneVsRestClassifier from scipy import interp导入数据: iris = datasets.load_iris() X = iris.data y = iris.target对训练标签做标签二值化运算(one-hot编码): # Binarize the output y = label_binarize(y,classes=[0,1,2]) n_classes = y.shape[1] n_classes 3对每个数据在尾部加入噪音: # Add noisy features to make the problem harder random_state = np.random.RandomState(0) n_samples, n_features = X.shape X = np.c_[X,random_state.randn(n_samples,200 * n_features)]注:np.c_ np.c_[random_state.randn(2,2),[[0,0],[1,1]]] array([[ 0.73381936, 0.26909417, 0. , 0. ], [ 1.07274021, -0.9826661 , 1. , 1. ]])划分数据集: # shuffle and split training and test sets X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=.5,random_state=0)fit一个分类器: # Learn to predict each class against the other classifier = OneVsRestClassifier(svm.SVC(kernel='linear',probability=True, random_state=random_state)) y_score = classifier.fit(X_train,y_train).decision_function(X_test)注:decision_function(X): Returns the distance of each sample from the decision boundary for each class. 计算每一个类别的ROC与AUC: # Compute ROC curve and ROC area for each class fpr = dict() tpr = dict() roc_auc = dict() for i in range(n_classes): # 取出来的是各个类的测试值和预测值 fpr[i], tpr[i],_ = roc_curve(y_test[:, i],y_score[:,i]) roc_auc[i] = auc(fpr[i], tpr[i]) #Compute micro-average ROC curve and ROC area #类总和的基础上平均的ROC 和 AUC fpr["micro"],tpr["micro"],_ = roc_curve(y_test.ravel(), y_score.ravel()) roc_auc["micro"] = auc(fpr["micro"],tpr["micro"])绘图: plt.rcParams['savefig.dpi'] = 300 #图片像素 plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 300 #分辨率 plt.figure() # linewidth lw = 2 plt.plot(fpr[2], tpr[2], color='darkorange', lw=lw, label='ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % roc_auc[2]) plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=lw, linestyle='--') plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0]) plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05]) plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate') plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate') plt.title('Receiver operating characteristic example') plt.legend(loc="lower right") plt.show()
|
【本文地址】